Optical and Physical Studies

Head of the department
Dr.Sc.
Roman V. BESSONOV
Labs
- Optical and Physical Measurement Techniques
- Onboard Imagery Processing Techniques
Новости
Head of the department
Dr.Sc.
Roman V. BESSONOV
Labs
- Optical and Physical Measurement Techniques
- Onboard Imagery Processing Techniques
Themes
Development of techniques and equipment for:
- spacecraft autonomous attitude control and navigation in outer space using natural physical fields and cues;
- imaging surface of the Earth, planets and small bodies of the Solar System from orbital and landing modules;
- pointing the spacecraft and scientific instruments on specific targets for the tasks of remote sensing, astronomy, and astrophysics.
In general
The Department develops methods and optical electronic equipment, which is used to monitor various objects on the Earth and in space, in the systems of technical vision and star attitude control and spacecraft navigation systems. This is one of the oldest IKI divisions, founded in the early 1970s.
The founder and the first head of the Department was Professor Yan L. Ziman (1922-2009), a veteran of the Great Patriotic War, awarded four combat orders and 14 medals, an honorary civil aviation navigator, a laureate of the USSR State Prize, an honored worker of science of the Russian Federation.
The Department took part in the following experiments:
- multispectral photography of the Earth surface (in several spectral bands simultaneously), followed by the development of automatic georeferencing methods using synchronous stars imaging (carried out from four manned Salyut stations and the spaceship Soyuz-22 – Raduga experiment, September 1976). The next steps in this direction were digital imaging (instead of analog) and automatic data processing, and as a result, multispectral imaging system Fragment-2 was created (Meteor - Priroda No. 3, 1980).
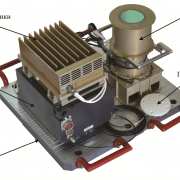
- In the early 1970s, the Department created an airborne system of remote-sensing instruments: multispectral and topographic cameras, optoelectronic scanners and infrared radiometers, digital data tape recorders.
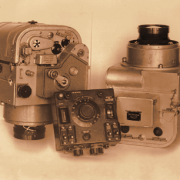
- In the 1980s, for the VEGA project focused on Venus and Halley’s Comet, the Department created a comprehensive set of instruments, which had to to identify the Halley’s Comet nucleus on approach and point the mobile platform with scientific instruments at it, following the nucleus during fly-by. Together with the Hungarian and French specialists a TV system VEGA was designed based on CCD arrays.
- At the same time since the early 1980s the Department initiated the design of widefield star trackers based on CCD-arrays and microprocessors capable to determine a spacecraft attitude by images of arbitrary sections of the celestial sphere. The Astro set of three optical star sensors, developed with the participation of Department’s specialists, was installed on the Mir manned station in 1986 and had been working successfully until the end of the station lifetime. In 2001 the station was de-orbited and flooded based on readouts of the trackers.
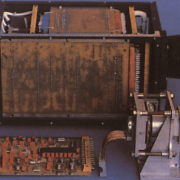
- A pioneering development of the Department was the star tracker BOKZ. It helps to determine a spacecraft attitude using the images of an arbitrary sky section. As of the end of 2020, more than 120 the BOKZ family star trackers were put into orbit aboard 53 spacecraft, 24 of which are in active operation. Their total operating time is over 4 million hours in total. About 50 other BOKZ devices are under development in IKI and spacecraft production plants at various stages.
Developments
| Solar and star trackers | Optical trackers |
|
|
| Remote-sensing instruments | Digital satellite cameras |
|
|
| Processors | |
|
|